Description
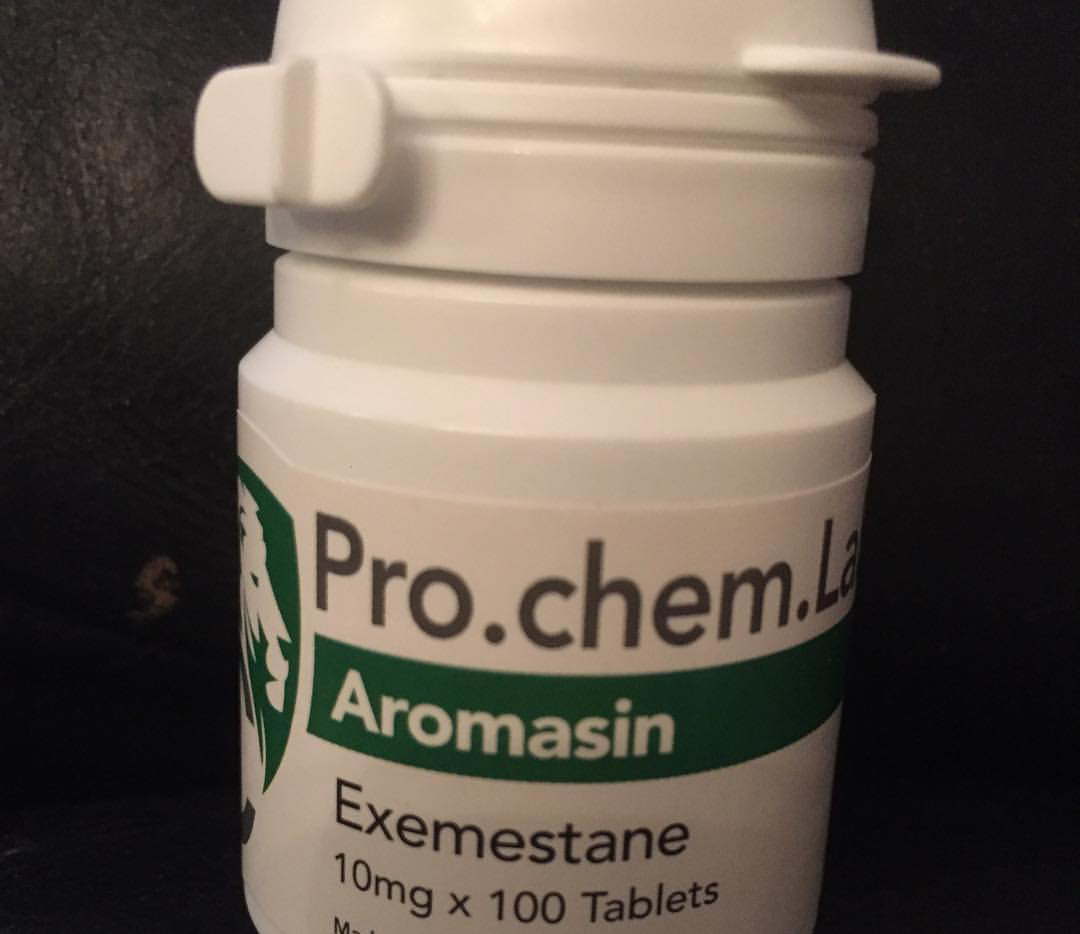
Aromasin Breast Cancer Treatment
Aromasin (Exemestane) is a prescription medication used to treat certain types of breast cancer, primarily in postmenopausal women. It is classified as an aromatase inhibitor, which works by decreasing the production of estrogen in the body, a hormone that can promote the growth of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer.
Key Information About Aromasin:
Uses:
- Breast Cancer Treatment: Aromasin is commonly prescribed for postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer. It is typically used after surgery or other treatments, such as chemotherapy, to reduce the risk of cancer recurrence.
- Early and Advanced Breast Cancer: Aromasin can be used for both early-stage breast cancer as well as advanced or metastatic breast cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
- Prevention of Recurrence: For women who have already been treated with another hormonal therapy (e.g., Tamoxifen), Aromasin may be used to further reduce the chances of cancer returning.
Mechanism of Action:
- Aromasin works by inhibiting the enzyme aromatase, which is responsible for converting androgens into estrogen in the body. By blocking this conversion, Aromasin lowers estrogen levels, which can help slow or stop the growth of hormone-dependent breast cancer cells.
Dosage and Administration:
- Standard Dosage: Typically, Aromasin is taken once daily, often in a dose of 25 mg. It is usually taken after a meal to improve absorption.
- Duration: The duration of treatment can vary but is often prescribed for 2 to 5 years, depending on the individual case.
Common Side Effects:
- Hot flashes
- Joint and muscle pain
- Fatigue
- Bone thinning or osteoporosis (long-term use)
- Nausea
- Increased sweating
Less Common but Serious Side Effects:
- Bone fractures
- Depression or mood changes
- Liver issues
- Cardiovascular problems (for those at risk)
Comparisons:
- Aromasin is often compared to other aromatase inhibitors like Letrozole and Anastrozole. While all three medications work similarly by lowering estrogen levels, they may have slightly different side effect profiles and efficacy rates.
Who Should Not Take Aromasin:
- Pre-menopausal women (since Aromasin is specifically for postmenopausal women)
- People with known hypersensitivity to Exemestane or any other ingredient in the medication.
Monitoring:
- Patients on Aromasin often need regular monitoring, including bone density tests (due to the risk of osteoporosis) and liver function tests.
Purchasing Aromasin:
In the USA, Aromasin is available through prescription and can be bought at pharmacies, including online options. Insurance coverage may vary, and generic versions (Exemestane) are typically more affordable.














Sadye –
Needed some gear since I decided to increase the length of my current cycle. I heard that this site is the best place to buy it from a friend of mine. I received everything and it all came well boxed and was packed safely. No problems with any of the postal service either. I will definitely place another order.
Zel Dalbor –
New customer here. This is the first time I purchased from this source as my usual source has gone off the grid and not replied to me in over a month and I needed to stock up for my next cycle. I am glad that they had what I wanted and since the reviews were saying great things about them, I was happy to ordered and after being tipped off I am very happy with my products.
Reatha Spearman –
Almost two months ago, I placed an order with them. And now that I’m far into my cycle, all I can say is that I adore their products, and the quality is unbeatable for the price.
Silas Ryder –
This is the firm from whom I’ve been ordering.
My orders are processed and shipped in a timely manner, and the products and prices are excellent.
Never let yourself down.
Ng Y lindo –
Customer service was quite helpful in resolving an uncommon circumstance. I would definitely suggest them and will undoubtedly use them again in the future. Thank you very much!
Johnson –
I’m familiar with the pro chem brand, so I know that the pro chem products from this site are genuine. I’ll have to update you with the other gear as I have yet to try it.
King Cole –
I have ordered 3 times . Every time I received my order in about a month, which is what I expected . I received regular shipping updates . I definitely recommend them and will continue.
Anth –
I recommend this website. I bought Aromasin and it is really effective for breast cancer with light exercises. And also the delivery was fast and excellent service! Keep it up, guys. I love the website so much! THANKS!
ORION –
I have been changing suppliers for pretty much every new order I had made until I found this site. Every penny spent here is well worth it and in the long run, you save on time, money, and putting your body through abuse. The gains I have achieved are wild and I just wanted to say thank you.