In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a complex series of procedures used to help with fertility, prevent genetic problems, and assist with the conception of a child. IVF is one of the most common and effective forms of assisted reproductive technology (ART).
It involves several steps, including ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, fertilization, embryo development, and embryo transfer. Here’s an overview of the IVF treatment process:
1. Initial Consultation and Testing
- Consultation with a fertility specialist: The first step involves meeting with a fertility doctor who reviews your medical history, previous fertility treatments (if any), and any factors that could affect fertility, such as age, underlying health conditions, or hormone levels.
- Pre-treatment testing: Both partners may undergo several tests, including:
- Ovarian reserve testing (AMH, FSH levels) to assess the woman’s egg supply.
- Ultrasound to check the ovaries and uterus.
- Semen analysis to evaluate sperm count, mobility, and quality.
- Blood tests to screen for infections, genetic disorders, or hormone imbalances.
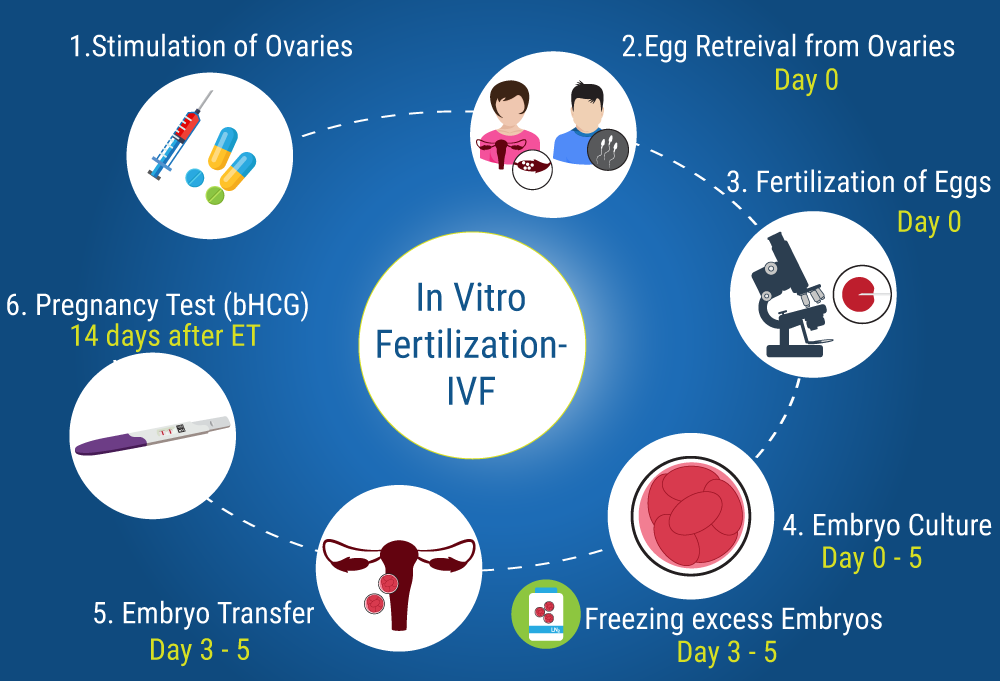
2. Ovarian Stimulation
- The first active step of IVF involves stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple eggs (instead of the usual one egg per cycle).
- Fertility medications such as Gonal-F (follitropin alfa), Menopur, or Follistim are injected daily to encourage the development of multiple follicles (egg-containing sacs).
- During this time, the response of the ovaries is carefully monitored with blood tests (to check hormone levels like estrogen) and ultrasound scans to track the growth of the follicles.
- This phase lasts about 8–14 days, depending on how the ovaries respond.
3. Trigger Shot and Egg Retrieval
- When the follicles reach an optimal size, a trigger shot (typically hCG, or sometimes Lupron) is administered. This shot stimulates the final maturation of the eggs and prepares them for retrieval.
- Egg retrieval is typically scheduled 36 hours after the trigger shot. This is a minor surgical procedure where a needle is inserted into each ovary (via the vaginal wall) to collect the mature eggs.
- The procedure is performed under sedation or light anesthesia and usually takes around 20–30 minutes.
- After the eggs are retrieved, they are immediately handed over to the embryologist in the IVF lab.
4. Sperm Collection and Fertilization
- On the day of egg retrieval, a sperm sample is collected from the male partner or a donor.
- In the lab, the sperm is processed and prepared for fertilization.
- Fertilization methods:
- Conventional IVF: The eggs and sperm are combined in a petri dish and left to fertilize naturally.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): A single sperm is injected directly into each mature egg. This is often used in cases of male infertility or previous IVF failures.
5. Embryo Development
- After fertilization, the embryos are cultured in the lab for several days. Usually, they are observed for 3 to 5 days to assess their quality and development.
- By day 5, the embryo reaches the blastocyst stage, which is ideal for implantation.
- Embryos are graded based on their appearance and development potential. The healthiest embryos are selected for transfer or freezing.
6. Embryo Transfer
- One or more embryos are transferred into the woman’s uterus, typically on day 3 or day 5 after retrieval.
- The embryo transfer is a quick, painless procedure that involves inserting a thin catheter through the cervix and placing the embryo(s) in the uterus.
- Excess healthy embryos can be cryopreserved (frozen) for future use.
7. Luteal Phase Support
- After embryo transfer, the woman receives progesterone supplements (through injections, vaginal suppositories, or pills) to support the uterine lining and help implantation.
- Progesterone is usually taken daily for about two weeks.
8. Pregnancy Test
- About 10–14 days after embryo transfer, a blood test is done to check for pregnancy by measuring levels of the hormone hCG.
- If the pregnancy test is positive, further blood tests and ultrasound scans are scheduled to monitor the progress of the pregnancy.
- If the test is negative, the doctor will discuss the next steps, which may include another IVF cycle or transferring a frozen embryo.
9. IVF Success Rates and Factors
- IVF success rates depend on various factors, such as:
- Age of the woman: Success rates are generally higher for women under 35.
- Egg and sperm quality: Healthy eggs and sperm improve the chances of fertilization and healthy embryo development.
- Underlying fertility issues: Conditions like endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), or unexplained infertility can affect success rates.
- Lifestyle factors: Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol, and managing stress can positively influence outcomes.
10. Risks and Considerations
- Multiple pregnancies: IVF increases the chance of twins or triplets, especially if multiple embryos are transferred.
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): Overstimulation of the ovaries can lead to OHSS, causing swollen, painful ovaries and, in severe cases, fluid buildup in the abdomen.
- Miscarriage: As with natural conception, miscarriage is a possibility, particularly in older women or those with underlying health issues.
11. Cost of IVF
- The cost of an IVF cycle can vary greatly, depending on the location, clinic, and whether the treatment is partially covered by insurance or government programs. In Australia, the cost can range from AUD 9,000 to AUD 15,000 per cycle, though Medicare rebates may reduce this amount.
IVF is a promising option for couples facing fertility challenges, offering a pathway to pregnancy when other treatments have failed. While it can be physically and emotionally demanding, the technology and success rates continue to improve.
- Fertility drugs for women
- Best fertility drugs for men and women
- Buy fertility drugs online
- Fertility medication for pregnancy
- Fertility treatment medication guide
- How fertility drugs work
- Top fertility drugs for ovulation
- Prescription fertility drugs
- Fertility medication for IVF
- Fertility drugs and side effects
Optional Steps and Considerations:
- Embryo Freezing: Any additional viable embryos can be cryopreserved for future use.
- Genetic Testing: Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) may be done to screen embryos for chromosomal abnormalities.
- Donor Eggs/Sperm: In cases of low egg or sperm quality, donor options may be considered.
Success Rates and Factors
The success of IVF depends on factors like age, egg and sperm quality, and underlying fertility issues. On average, the live birth rate for IVF is higher in younger patients.
Step-by-Step IVF Process
- Initial Consultation and Testing: You meet a fertility specialist to discuss medical history and undergo tests like ovarian reserve evaluation, uterine cavity assessments, and semen analysis if applicable. Genetic screening may also be conducted
Considerations and Preparation
Preparation includes health assessments, supplements like folic acid, and personalized treatment plans based on age and medical history. Side effects may include mild bloating or cramping post-procedures
.
For more detailed insights, you can visit resources like
ps:/
ep-by-step-ivf-process/) or Cleveland Clinic.









You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this topic to be actually something that I think I would never understand. It seems too complex and extremely broad for me. I am looking forward for your next post, I will try to get the hang of it!
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.